WARNING! The information and photographs contained in this guide are quite explicit and may be disturbing to some viewers. By entering our site, you agree that you are either an adult, or have your parent or guardian’s permission to view explicit information and images on the internet. Please review our user agreement and medical disclaimer before going any further. IN NO WAY SHOULD AFRAIDTOASK.COM’S SITE OR ONLINE GUIDES BE CONSIDERED AS OFFERING MEDICAL ADVICE!
Sexuality is a crucial aspect of human life and functioning. Many issues, both physical and mental are interwoven together to form our sense of sexuality. This online guide focuses on some of the physical aspects regarding sexuality, namely illness and disease associated with sexual activity. Though some of the photographs and depictions that follow may be uncomfortable for those unaccustomed to such graphic medical images, keep in mind that all of these disease states are avoidable, treatable, and many are curable. Click here to locate a health center in your area for testing and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases. The absolute best “cure”, however, is PREVENTION (i.e., not getting the disease in the first place). Abstinence is the only foolproof way of avoiding a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Condom use is another way to avoid these diseases (though the condom must be worn at each and every sexual encounter, and there must be no exchange of any bodily fluids). We should mention that the new politically correct term for STD is STI (Sexually Transmitted Infection); we will use the older “cruder” term throughout this guide as this is the phrase most surfers know. Thank you for your support. When you are ready to leave the site, please consider filling out our anonymous survey; we take your comments seriously. The paintings, Adam and Eve, are two pieces done by Albrecht Durer in 1507. Adam holds in his left hand a branch of the apple tree, the fruit of sin, while Eve stands close to the tree where the tempting snake coils.
ANATOMY
The detailed anatomy of the male and female genitalia is quite complex, and beyond the scope of this online guide. Below are the basic structures mentioned in this guide.
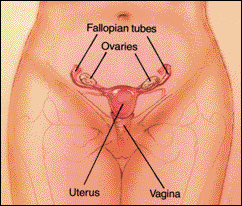
EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF WOMAN (Front View)
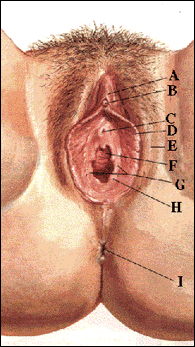 |
A: Prepuce (Hood) of ClitorisB: Clitoris C: Opening of Urethra (urinary tract) D: Labia minora E: Labia majora F: Opening of Vagina G: Vestibule H: Hyman tissue (residual) I: Opening of Anus |
INTERNAL ANATOMY OF WOMAN
 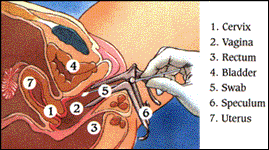 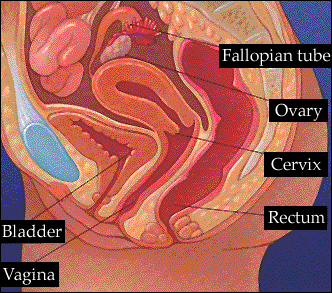 |
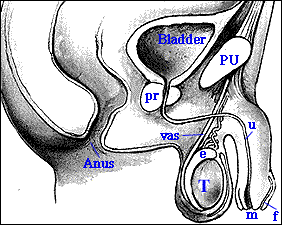
EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF MAN
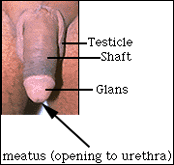
INTERNAL ANATOMY OF MAN (CROSS-SECTION VIEW)
CHLAMYDIA
What is it?
Chlamydia is actually a group of different infections caused by different strains of the Chlamydia bacterium. Though Chlamydia pneumonia can cause a type of walking pneumonia, and Chlamydia psittaci can cause a type of pneumonia caused by birds, it is Chlamydia trachomatis that causes various sexually transmitted diseases. Chlamydia is currently the most common STD.
(Compare this discharge to that seen in gonorrhea.)
Common Signs & Symptoms
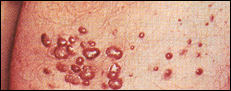
Chlamydia can cause asymptomatic (no symptoms) infections in both men and women. In men it can cause groin pain and swelling (epididymitis) as well as burning on urination (so called, non-gonoccocal urethritis (NGU)). In prepubertal girls, it can cause a mild vaginal discharge and odor (called vaginitis); in postpubertal women it can cause an off-white discharge and odor which comes from an infected cervix. In women, it can be especially dangerous because it can silently linger for months and progress to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) which can lead to infertility, chronic pain, and even death. Even babies can get this infection: one half of all babies being delivered through the birth canal of an infected women will develop a Chlamydial conjunctivitis (pink eye) a week after birth. About a quarter of babies passing down the infected birth canal will get a Chlamydia pneumonia. Certain strains of Chlamydia trachomatis can get into the skin through minute cuts and cause a disease known as Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV). This disease has a number of stages from a mild swollen groin lymph node to fever and chills. After months to years, LGV can spread to other lymph nodes causing pain, swelling, skin breakdown (ulceration as pictured) and other problems involving ones rectum and genitals.
How’s it Diagnosed?

Diagnosis is made by isolating the Chlamydia bacteria in a culture, or by finding evidence of the bacteria’s unique DNA in a urine or vaginal sample. On women, a speculum exam is performed by the doctor; a cervical sample is obtained and sent to the laboratory for analysis. In men, a smaller swab will be inserted in the meatus (or, newer studies are showing that a urine sample can be used instead.)
How’s it Treated?
A number of antibiotics in the Erythromycin family will kill and hence cure Chlamydial infections. The trick is to get diagnosed, as quite commonly those infected are unaware.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Abstinence or correct condom use will prevent transmission of this bacteria from one person to the next. Pregnant women who have had more than one sexual partner should be checked by their physician to be sure they do not have an asymptomatic infection.
Additional Information
Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
GENITAL WARTS (HPV)
What is it?
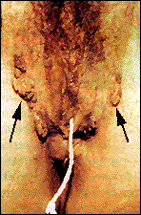
HPV is known by many names including venereal, anogenital, or genital warts, and condylomata acuminata. It is a viral infection of skin causing the growth of skin-colored, cauliflower-like masses of various sizes and shapes as shown by the arrows in this picture. (A tampon string is in place as she was menstruating at the time this photo was taken.) It has become very common over the last two decades infecting anywhere from 3% to 28% of the population.
Common Signs & Symptoms
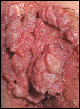
Several weeks to months after being exposed to a sexual partner with HPV, these painless growths occur on damp or moist surfaces in either sex. Common locations include those pictured as well as around the anus. They often begin as tiny red spots and can grow quickly into cauliflower-like masses. Infection of a woman’s cervix with certain strains of this virus can lead to cervical cancer. It is crucial, therefore, for all women who have this disease to have regular pap smears. (Actually, all women who are sexually active need to have regular pap smears to look for cervical problems.)
 |
 |
|
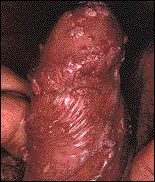
HPV of the penis
|
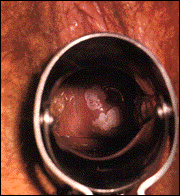
HPV on the cervix (looking into the vagina through a speculum)
|
How’s it Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made when a physician sees the classic-shaped growths. If there is any question, a sample of the abnormal tissue (biopsy) can be taken and sent to the lab for microscopic analysis. Cervical HPV is diagnosed by taking a small sample of cervical cells with a popsicle-like stick (pap smear) and preparing this specimen on a slide for microscopic analysis.
How’s it Treated?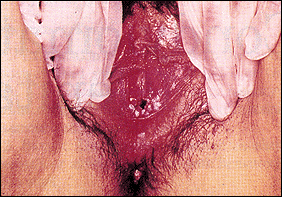
Like most viral infections, there is no cure for Human Papillomavirus. Treatment consists of destroying the infected cells, but it often comes back due to infection of normal-appearing nearby skin. If left untreated, genital warts may go away on their own. One study showed that nearly 1/3 of all patients had spontaneous resolution of the growths. For those not wanting to wait to see if they disappear on their own (e.g., most people), destruction of the abnormal cells can be done via a number of methods such as freezing the growths with liquid nitrogen, destroying the tissue with laser surgery, using a blistering agent (such as podophyllin – made from rain forest beetles), or burning them off with a potent acid (e.g., trichloracetic acid). A doctor trained in one of these techniques should be seen to prevent damaging the normal surrounding tissue. A novel approach is to enhance ones own immune system to fight off the genital warts. One such “immune-enhancer” is a cream called imiquimod (Aldara). Imiquimod is currently available by a doctor’s prescription only, but unlike the other treatments that require a health professional to apply, Aldara is applied by the patient themselves, in the privacy of their own home. The patient puts a small amount of the cream on the warts three times a week. Aldara is for the treatment of visible warts on the genitals and perianal area. It is not for treatment of cervical or intravaginal warts. Cervical or intravaginal warts are usually treated with freezing or by surgically removing the infected area.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Abstinence, and correct condom use may prevent transmission of this virus from one person to the next. A vaccine called Gardasil can prevent the types of genital warts that cause cervical cancer. It is crucial that all infected skin be covered to prevent skin to skin transmission. Since multiple areas of skin touch during intimate encounters, condom use is not terribly effective.
Additional Information Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
GONORRHEA
What is it?
Gonorrhea is a common infection of the genitourinary tract (specifically the urethra and cervix) caused by the bacteria, Nisseria gonorrhoeae. About 1 million new infections are reported each year in the United States. Young men aged 20 – 24 have the highest rate followed by those 15 to 19 years old. In women, the highest rate are in adolescents aged 15 – 19 years old. It is also quite common to have both Gonorrhea and Chlamydia infections at the same time. In 130 AD, Galen named the condition Gonorrhea (latin for “flow of seeds”), because the condition was associated with urethral discharge in men.
(Compare this discharge to that seen in chlamydia.)
Common Signs & Symptoms
Getting gonorrhea occurs following unprotected sexual contact with somebody who is already infected. Children born to infected moms can get gonorrhea of the eyes during the baby’s passage through the birth canal.
MEN (pictured): Though many infected males may not have any symptoms, usually 3 – 6 days after infection one gets symptoms of urethritis (inflammation of the urethra). This includes BURNING WHEN PEEING, GOING MORE OFTEN THAN NORMAL, AND A PUS DISCHARGE FROM THE PENIS. Other symptoms include a red and swollen meatus.
WOMEN: Most infected women do not get symptoms, though a greenish-yellow vaginal discharge may come from the cervix. Other symptoms may include an itchy and red vulva. The most dangerous aspect of this infection is in women who develop gonorrhea of the uterus and fallopian tubes. This common cause of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) can lead to severe pain, fever, infection of the whole body, infertility (the inability to have children), and even death!
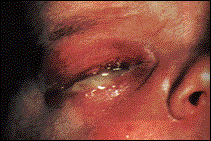
CHILDREN: Newborn infants can get Gonorrhea eye infection (conjunctivitis) as they pass through an infected mother’s birth canal. This leads to terrible pus and potential blindness if not treated. This is one reason ALL newborns get an antibiotic ointment put into their eyes immediately after being born. The antibiotic ointment kills both Gonorrhea and Chlamydia neonatal conjunctivitis.
How’s it Diagnosed?
A culture from the site of infection (e.g., urethra, cervix, rectum, throat, eye) grown with a special bacteria food (Thayer-Martin growth medium) usually allows a diagnosis to be made. Cultures are obtained by “swabbing” the infected area.
How’s it Treated?
Gonorrhea used to be 100% curable with Penicillin. Unfortunately, because antibiotics have been used so commonly (often given out for simple colds – where they don’t do anything) that the gonorrhea bacteria has developed RESISTANCE! We now use a more potent antibiotic to cure gonorrhea. Usually a shot of ceftriaxone (Rocephin) or an extra-large dose of azithromycin (Zithromax) will kill the bacteria and cure the disease. It is crucial that those infected alert their sexual partners to allow them to be adequately treated.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Avoidance by abstinence, or good use of a condom during sexual relations is the surest way of avoiding this disease.
Additional Information
Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
HEPATITIS B
Hepatitis B virus is one of the viruses that causes hepatitis, or inflammation of the liver. It is spread by contact with infected blood or body fluids (sperm, vaginal secretions, pus, tears, saliva, etc.) commonly exchanged during unprotected intercourse. Hepatitis B is the most common chronic infectious disease in the world! Most of the 300 million people infected live in Asia and Africa, though 1.5 million are in the United States.
Common Signs & Symptoms
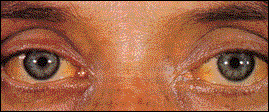
Hepatitis B virus is one of many causes of hepatitis, a swelling of the liver. The liver plays a crucial role in cleaning the blood and metabolizing different substances we ingest. When the liver isn’t working correctly, “poisons” build up in the blood. In addition, the liver makes bile, and if it isn’t released correctly, it builds up in the body causing a yellowing of the skin and eyes (called jaundice and icterus, respectively-pictured). People first infected with HBV commonly get flu-like symptoms with body aches, fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. In the majority of adults, HBV infection then goes into a remission without any signs or symptoms. In 10% (1 out of 10) of teenagers and adults, the HBV infection will become chronic (long term). Chronically infected people are at a high risk of developing liver failure (cirrhosis) and liver cancers (hepatocellular carcinoma), which can lead to death. In infants who acquire HBV from their infected mother, 90% will have chronic hepatitis.
How’s it Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by a blood test. All pregnant women are routinely tested as the easiest way to get this disease is by getting it from your mother while being born.
How’s it Treated?
Currently there is no cure for Hepatitis B, though promising research is underway. Interferon, ribavirin, and lamivudine, are the most common options currently used by physicians treating chronic hepatitis B. Prevention of this disease, however, is the goal.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
The best protection is by getting immunized. Currently all newborn babies in the U.S. are offered this three-shot vaccination series. Adolescents and teenagers can also get vaccine series free from their state (by going to their family physician or pediatrician). Adults can also be vaccinated, though most healthy condom use will usually prevent transmission of this virus from one person to the next by sexual contact. insurances will not pay (the cost is approximately $50/shot X 3 shots = $150). Abstinence or correct
Additional Information
Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
HEPATITIS C
Hepatitis C virus is one of the viruses that causes hepatitis, or inflammation of the liver. It is spread predominantly by contact with infected blood and much less commonly, body fluids (sperm, vaginal secretions, pus, saliva, etc.) Risk factors for having HCV include those who have used IV drugs (e.g., those who have shared needles), those who have received a blood transfusion prior to 1991, those who have snorted cocaine*, and those who have been tattooed.
Unlike HBV, sexual transmission of HCV is very uncommon and is estimated to occur in less than 5% of those in monogamous relationships. That said, the risk of HCV is increased in those having multiple sexual partners and unprotected intercourse. There seems to be no increased risk of HCV in men who have sex with men. Therefore, while using a condom if having sexual relations is just plain smart, in terms of HCV infection, avoidance of exposure to infected blood (e.g., avoid sharing razor blades, toothbrushes, and bloody needles) is the most important method in avoiding infection.
Common Signs & Symptoms

Hepatitis C virus is one of many causes of swelling of the liver (hepatitis). The liver plays a crucial role in cleaning the blood and metabolizing different substances we ingest. When the liver isn’t working correctly, “poisons” build up in the blood. In addition, the liver makes bile, and if it isn’t released correctly, it builds up in the body causing a yellowing of the skin and eyes (called jaundice and icterus, respectively). People first infected with HCV commonly get mild flu-like symptoms with aches, fever, and chills. Following this flu-like illness, however, symptoms generally resolve for more than 2 decades! Though a number of people infected with Hepatitis C go on to remission, a much larger portion of infected individuals will have worsening liver disease and will get sicker years later. Those who are chronically infected are at a high risk of developing total liver failure (cirrhosis) and liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma), both of which can lead to death.
How’s it Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by a blood test. Because people infected generally have NO SYMPTOMS for 20 or more years following infection, it is important to get a screening blood test if you have any risk factors for HCV infection. You should be tested specifically for the presence of HCV antibody if you have used IV drugs, received a blood transfusion prior to 1991, snorted cocaine, been tattooed, or had multiple sexual partners. While it is reasonable for the spouse or sexual partner of an HCV-infected person to be tested, other household members or coworkers do not have an increased risk of catching HCV. (Screening liver function tests are not adequate to test for this disease as they are commonly normal in infected individuals. A HCV antibody test is the recommended blood test.)
How’s it Treated?
Exciting new treatments have recently been developed which can markedly improve the disease, and perhaps even cure, some people with Hepatitis C Virus. A combination of interferon and ribavirin (Rebetol) has been shown to be quite effective in a number of recent studies. Despite these recent successes, prevention of this disease is much preferred by avoiding risk factors.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Avoiding the risk behaviors mentioned previously is important (e.g., snorting cocaine, using IV drugs, and having unsafe sex with multiple partners).
Additional Information
Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
*While relatively low risk, those who have snorted cocaine do have a somewhat higher risk of being infected with HCV than those who have never snorted cocaine, and should therefore have an HCV antibody test as a screening measure.
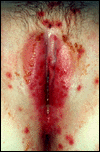
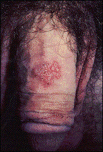
HERPES
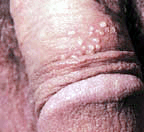
What is it? Herpes is a viral infection of the skin caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV).Classically, HSV-1 caused a mouth and lip rash (i.e., cold sore – pictured below), while HSV-2 caused the genital herpes. Over the last decade, it has become clear that either strain of this virus can cause either rash, though 75% of genital herpes is caused by HSV-2. One in five of us in the general population has genital herpes while almost three out of four people have a history of cold sores caused by the Herpes virus. As expected, one’s sexual history determines the prevalence of the genital form of this infection. In other words, while only 3% of nuns have genital herpes, 80% of prostitutes have it.
Common Signs & Symptoms Herpes is spread by skin-to-skin contact. Unfortunately, most exposure occurs when there is no identifiable rash (e.g., when the person is asymptomatic) as there is shedding of the virus through the skin about 1% of the time. (Click on the images for a more detailed view.)
 |
 |
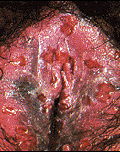 |
After exposure to the virus, a 2 to 20 day incubation period ensues followed by the primary genital herpes outbreak. Only 50% of those infected will have significant enough symptoms to know they are infected. Symptoms of primary genital herpes may include fever, headache, and muscle aches followed 3 days later by the classical rash (pictured) of painful blisters and ulcerations of the skin where the infection occurred.
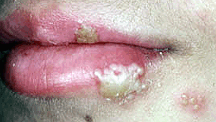
Tender and swollen groin glands (lymph nodes) then develop about a week after the skin rash. The rash and pain usually completely goes away over 3 to 4 weeks.Unfortunately, the virus then hangs around in the nerves, often causing a reinfection from time to time. This recurrent genital herpes usually begins with a burning or itchy sensation 1 – 2 days before the skin rash develops. Recurrent herpes is less painful and less severe than the primary infection. One terrible manifestation of this viral infection occurs in babies delivered through the birth canal of an infected woman. Though relatively rare in women who are not having an outbreak at delivery, neonatal herpes (infection of the newborn) often causes a whole-body and brain infection in the baby. There is a high death rate for infants infected and of those that live, there is often residual mental retardation and blindness. To decrease the risk of this awful disease, a Cesarean (C-section) delivery should be done in pregnant women who go into labor and have a genital herpes outbreak at the same time.
How’s it Diagnosed? Diagnosis is made by a physician when hearing the symptoms of the rash and examining the blistered area. If there is any question, a sample of the abnormal tissue (biopsy) can be sent to the lab for microscopic analysis. A viral culture of the wound can also be checked to verify the presence of the Herpes Simplex Virus.
How’s it Treated? Like most viral infections, there is no cure for Herpes. Anti-viral medications have come to market lately and have done a very good job at improving the duration of an outbreak as well as the discomfort. Medications such as acyclovir (Zovirax), famcyclovir (Famvir), valacyclovir (Valtrex), and others can significantly lessen the pain and symptoms and shorten the course of the herpes outbreak. The pills can also be used to prevent recurrences. Though technically used for genital herpes only, these medicines are commonly given at the first sign of an oral herpes sore to shorten the course and pain. Intravenous acyclovir is used in newborns infected during delivery.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)? Abstinence will prevent transmission of genital herpes from one person to the next. Using condoms correctly (covering all the infected skin areas), and avoiding sexual activity when sores are present will significantly decrease the risk of infection, but will not entirely eliminate the risk. An exciting new preventative technique is also quickly approaching. A number of studies have found a vaccine against herpes is effective in women (interestingly, the studies show no real benefit for men). Within the next year, it is quite likely that younger women may begin to be vaccinated with this herpes vaccine to decrease the risk of catching this viral infection. Ask your doctor, or contact SmithKline Beecham (manufacturer of this vaccine) for more info and on the status of this vaccination. Additional Information Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
HIV & AIDS
AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Over time, the HIV virus weakens the immune system by infecting and killing certain white blood cells. It is only after the immune system is significantly weakened that people with HIV get one or more “opportunistic” infections. Before this happens, there are essentially no symptoms or signs that indicate that somebody is infected with HIV. Magic Johnson has become an unofficial spokesman for this disease. A vigorous and healthy man living with HIV, he got infected through heterosexual intercourse and now is a major force in educating people about this disease.
It often takes many many years for somebody infected with HIV to have their immune system weakened to the point where these opportunistic infections (and unusual cancers) can occur. Once somebody begins to get these infections, they are said to have AIDS.
The disease was first defined by the CDC (Centers for Disease Control & Prevention) in 1981. It is estimated that over a million Americans are infected with HIV (one in every 250 people). Over 20 million people are infected worldwide. In some areas of Africa, 1 out of every 2 people have HIV! Though this disease was first thought to infect only homosexuals and IV drug users who share needles, it has since become clear that anybody exchanging bodily fluids (e.g., blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and possibly even saliva) can get this infection. Most of the continual spread of HIV is caused by unprotected heterosexual sex, followed by homosexual sex, IV drug use, and transmission to a baby by an infected mother.
Early HIV diagnosis and entry into health care system have both individual and societal benefits: improved health and productivity, reduced hospitalization costs, and decreased transmission from persons who do not know their HIV status. First, those who learn of their infection can take steps to avoid infecting others. Second, early treatment with new anti-viral medicines can slow the progression of the disease. Third, many of the opportunistic diseases can be prevented before they occur by using antibiotics and other medicines.
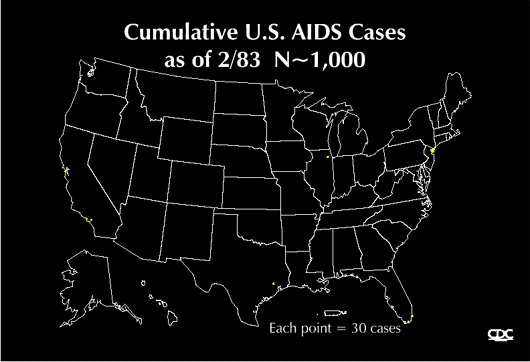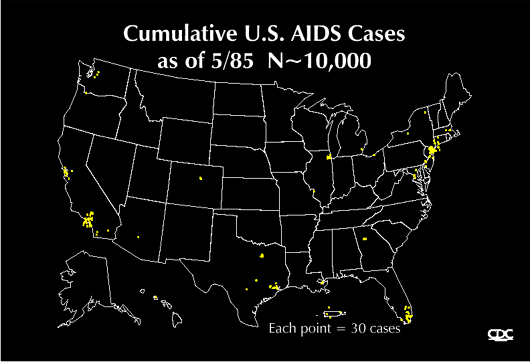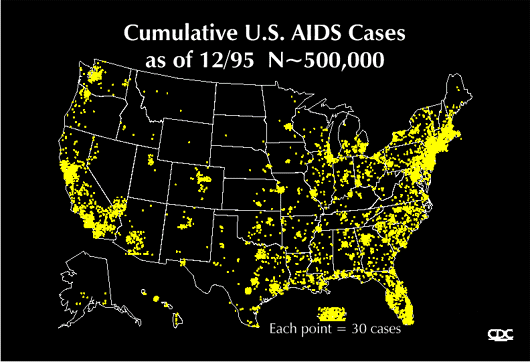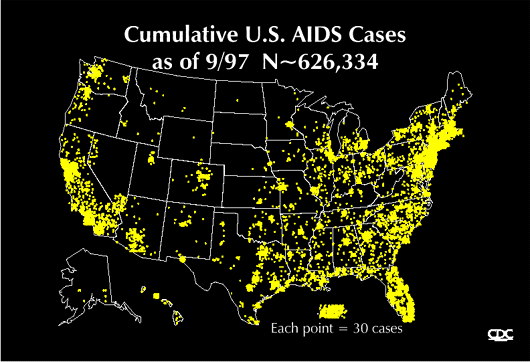
Early diagnosis of HIV is absolutely critical, so getting tested by your doctor is important if you have any risk factors, including a history of sharing needles, a history of unprotected heterosexual intercourse, if you are a man who has sex with men, or if you had a blood transfusion prior to 1987. Only blood, semen, vaginal fluid, breast milk, other body fluids containing blood, have been proven to spread HIV. (It is felt to be particularly unlikely that one can catch HIV through contact with saliva) You don’t catch HIV from talking to, working with, shaking hands, hugging, or kissing people who have HIV or AIDS!
A huge amount of ongoing research is being done to find a vaccine to prevent non-infected people from getting HIV if exposed, as well as finding better treatments and cures for those already infected. Though excellent and continually improving treatment is prolonging life and slowing the course of this disease, HIV infection is still considered to be nearly 100% fatal (even the Ebola virus isn’t that vicious)!
|
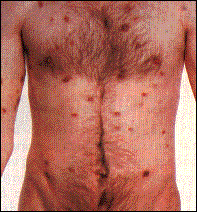
|
Kaposi’s sarcoma on the trunk and leg of a patient with AIDS
|
Common Signs & Symptoms
The signs & symptoms of HIV and AIDS are very different depending on how damaged ones immune system has become. When somebody initially gets exposed and infected by HIV, they often have flu-like symptoms (fever, chills, feeling lousy, swollen glands, etc.). These symptoms go away, and most people have no idea they have this infection until they are diagnosed with a blood test or they develop an opportunistic infection or unusual cancer.
The most common opportunistic infections include, Candida albicans (caused by a fungus) throat and body infection, Pneumocystis carinii (caused by a bacteria) pneumonia, Toxoplasmosis (caused by a fungus) brain infection, Cryptococcus (fungus) brain and body infection, Tuberculosis (bacteria) lung and body infection, Cytomegalovirus (CMV, virus) eye and body infection. The most common cancer associated with AIDS is called Kaposi’s sarcoma. Many other infections (such as Herpes, HPV, Streptococcal pneumonia, and Salmonella) occur in people with AIDS.
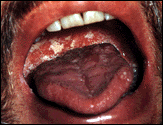 |
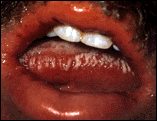 |
|
Throat infection with
Candida albicans (thrush) |
Oral Leukoplakia
|
How’s it Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by a blood test that finds antibodies against HIV (meaning you have been exposed to the virus and your body has developed an immune response and is making antibodies in an attempt to fight off the infection). Many times, people first learn they have AIDS when they go to their doctor with one of the common opportunistic infections or Kaposi’s sarcoma.
How’s it Treated?
Currently there is no cure for HIV infection. Treatment is geared towards both controlling the virus and treating the opportunistic infections. Many new and exciting anti-viral medications have had good success in slowing down the progression of HIV infection by preventing the virus from multiplying. Medications such as AZT, ddI, ddC, and the newer protease-inhibitors have gotten a lot of press since HIV was defined. Newer, less toxic, and better medications are continually being introduced and even more are on the way. Vaccine studies are underway both for those uninfected (i.e., the general population) and those already infected (to boost the immune system). Taking good care of oneself (eating healthily, exercising, etc.) also seems crucial in preventing the rapid progression of HIV. Pregnant women who have HIV infection should be treated with medicine during their pregnancy AND at delivery as this has been clearly proven to markedly reduce the rate of transmitting the infection to the baby.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Avoiding exposure to bodily fluids (blood, semen, vaginal secretions, etc.) is the surest way to avoid getting HIV. Abstinence or correct condom use with a latex condom will prevent transmission of HIV from one person to the next. Pregnant women who have HIV infection should be treated with medicine during their pregnancy AND at delivery to minimize the risk of spreading it to their baby.
LICE & CRABS

The most common parasites that infect humans are lice (Pediculus) and mites (Scabies). These are transmitted by personal contact, including sexual contact. Pubic lice (Phthirus pubis, or the crab louse) infestation is most common in adolescents and young adults. It is an infestation of hair-bearing areas, especially the groin. Though it is usually spread by sexual contact, lice can be spread by contact with contaminated items and clothing, such as towels.
An adult louse gets onto the skin and lays eggs. 6 to 10 days later, the eggs hatch releasing baby lice (nymphs) that grow into adults and multiply again (usually within 15 days). Both nymphs and adult lice feed on human blood.
Common Signs & Symptoms
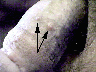
Intense itchiness at the infected area (usually the groin, anus, and abdomen areas) is the most common symptom. Often the itchiness is worse at night. Small red or bluish irritations of the skin are often seen. Crab eggs (nits) attach to hair and appear as tiny white-grey specks. Sometimes the crab louse can be seen moving within the pubic hair. Public lice can also infect other hairy areas (eyelashes, etc). The photograph (below right) shows irritated and inflamed skin caused by crab lice bites. Closer examination would show nits (eggs) on his pubic hair. The other photo shows a crab louse (arrow). Click on the images to see it more clearly.
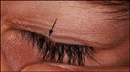 |
 |
How’s it Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by observing either the characteristic shape of the louse or nits (eggs).
How’s it Treated?
Treatment is with anti-parasite medication (e.g., Lindane or Permethrin). Re-treatment may sometimes be necessary if symptoms continue or recur. It is crucial that all bedding and clothing be decontaminated with hot-water machine washing (or dry cleaning) or else reinfection will occur.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Avoiding contact with infected individuals is how one avoids this uncomfortable infection. Even correct and consistent condom use does not prevent crab infection because infected pubic hair and skin come into contact with one’s partners pubic hair and skin.
Additional Information
Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
MOLLUSCUM

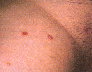
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign viral infection of the skin causing small skin-colored bumps. With the exception of not looking like normal skin, molluscum is not particularly harmful or painful. Some skin cancers may look like molluscum, so it is important to let your doctor examine you if you find any abnormal lumps or bumps. Molluscum is caused by a poxvirus. 2 to 7 weeks after being exposed, one may develop the classical skin rash.
Common Signs & Symptoms
Molluscum causes normal skin to grow into bumps. These are painless small bumps that often have a central divot (umbilication). There is no pain or discharge from these unless they are accidentally cut, and then they may bleed a bit. Molluscum is spread by direct contact with infected skin and can be spread to oneself and/or other people.
How’s it Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by observing the classical skin lesion (the small bump with central divot (umbilication) as seen in these photographs.
 |
 |
 |
How’s it Treated?
Molluscum is treated by destroying the infected skin. Destruction of the abnormal area can be done by freezing the growths with liquid nitrogen. Other techniques include destroying the tissue with laser surgery, using a blistering agent (such as podophyllin – made from rain forest beetles), or burning them off with a potent acid (trichloracetic acid). A doctor trained in one of these techniques should be seen to prevent damaging the normal surrounding tissue.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Abstinence or correct condom use may prevent transmission of this viral infection from one person to the next if the lesion is on the penis. Molluscum is not limited to the genital area and this disease is not necessarily sexually transmitted, so direct contact with anybody who has it can lead to infection.
Additional Information
Additional information on this, and other sexually transmitted diseases, can be found by clicking here.
PID
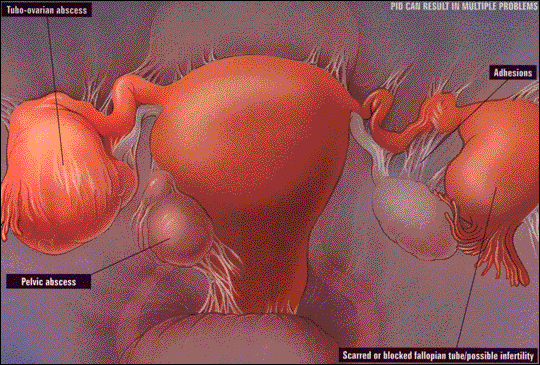
What is it?
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, or PID for short, is actually a spectrum of diseases that affect women only. The uterus, fallopian tubes, and other areas of a woman’s upper genital tract become infected and inflamed causing pain, swelling, fever, and scarring. The real significance of PID is that getting it causes changes in the normal anatomy of the woman’s genital tract thus increasing the future risk of an ectopic pregnancy (where an embryo grow outside of the uterus leading to shock and death of the mother if not rapidly diagnosed) and/or infertility (an inability to get pregnant). 10% to 30% of women will lose the ability to become pregnant after just one episode of PID! PID rates are highest among sexually active adolescents. Other risk factors include multiple sex partners, use of an IUD (intrauterine device for birth control), douching, and a prior episode of PID.
Common Signs & Symptoms
The most common symptom is abdominal or pelvic pain. Abnormal vaginal bleeding, pain during intercourse, and unexplained vaginal discharge are also common symptoms in PID. PID can be caused by a number of different bacteria. The most common ones are Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis, so PID often has similar signs and symptoms as these diseases. Other non-STDs have also been implicated in this disease (e.g., PID is not necessarily sexually transmitted, though the vast majority are caused by gonorrhea and chlamydia). Pelvic pain and fever with symptoms of gonorrhea or chlamydia are common symptoms as well.
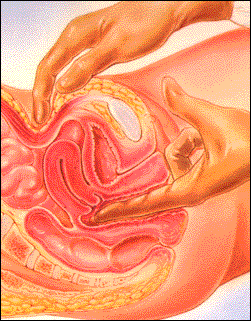
How’s it Diagnosed?
A thorough exam by a physician or qualified health care worker is necessary to diagnosis this disease. On the bimanual pelvic exam (a part of a woman’s physical examination where two hands are used to feel the anatomy of the pelvis), the doctor may find pain when examining the cervix (known as cervical motion tenderness or the “chandelier sign”). Diagnosis of gonorrhea or chlamydia in the presence of pelvic pain or cervical motion tenderness alerts the doctor to this diagnosis. A surgical procedure (laparoscopy) is rarely required to make the diagnosis.
How’s it Treated?
PID is treated with antibiotics. Because it is often unclear which bacteria is the actual one causing the disease, two or more antibiotics are often used together to cover, or kill, the majority of potential bacterial culprits. Many times, a patient with PID will be admitted to the hospital for intravenous (IV) treatment.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Abstinence or correct condom use will prevent transmission of the bacteria that causes PID, from one person to the next. Because men are often silent carriers of these bacteria, any male partner of a woman diagnosed with PID should see a doctor to be examined and checked for a sexually transmitted disease.
Additional Information
Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
SYPHILIS
What is it?
Syphilis is an ancient illness first described in the 15th century. It is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacteria, Treponema pallidum. This infection has been increasing in the world, infecting 20 people out of every 100,000. It has been especially prevalent in large cities.
Common Signs & Symptoms
Syphilis is a three-staged disease. In the first stage (“primary syphilis”), one or more painless skin ulcers (chancres), form at the site of inoculation.
| Primary Syphilis (Chancre) | |
Two to eight weeks after the chancre heals, “secondary syphilis” begins. In this stage, the Treponema bacteria spreads throughout the body causing many possible types of rash, including the palm rash seen in the photo below. Commonly the rash is found on the palms and soles.
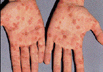 |
|
Secondary Syphilis
|
Because the rash can take so many different appearances, syphilis has been called “the great imitator”. A fever, sore throat, swollen glands, and just feeling lousy often occurs with secondary syphilis. Like primary syphilis, the signs & symptoms of secondary syphilis go away on their own.
Syphilis then becomes quiet (latent) for many years (with possible flares of secondary syphilis symptoms occurring from time to time). “Tertiary”, or late syphilis, often occurs 15 years or so after the initial chancre, and slowly gets worse and worse. It affects the brain and spinal cord, often causing mental illness and paralysis. It can also affect the heart causing inflammation of the aorta, and the deeper skin causing “gummas” which are rubbery lumps in the skin. In patients with HIV, many of the above classical signs & symptoms are not present, or are quite different.
Like many of the sexually transmitted diseases, a pregnant mother with syphilis can give it to the baby while in the womb. So called, congenital syphilis, can cause the baby to die before it is born (stillbirth). In those babies who survive, symptoms can involve the eyes, teeth, bones, liver, glands, lungs, and brain.
How’s it Diagnosed?
Syphilis is spread by touch of a chancre or one of the secondary rashes.These rashes are teeming with the bacteria. Diagnosis is made by taking a sample from the chancre and finding the cork-screwed shaped spirochete bacteria under the microscope (pictured).In those already in the latent phase, blood tests (RPR, VDRL, and FTA-ABS) can also alert the doctor to an infection. (All pregnant women have one of these blood test done, and many states still require one of these blood tests done before a marriage license will be issued.) Obviously, all sexual partners exposed to somebody with syphilis should be contacted and tested for the illness.
How’s it Treated?
Penicillin is still the first choice treatment in every stage of this illness, and usually cures the disease. Careful follow-up by the doctor is needed to be sure the disease is cured and does not return.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Abstinence or good condom use is the key to avoiding this disease. As any skin exposed to a chancre or other syphilitic rash can become infected, condoms are not always effective.
Additional Information
Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
TRICHOMONAS
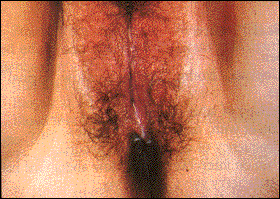
Trichomonas is caused by a single-cell parasite, Trichomonas vaginalis. First discovered in 1836, it has proven to be quite a common sexually transmitted disease. It is found in 50% – 75% of prostitutes and 5% – 15% of women seen in gynecology clinics. Since the parasite rarely causes symptoms in men, reinfection of women by their untreated partners is common.
Common Signs & Symptoms
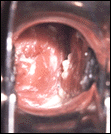
Trichomonas infection frequently has no symptoms. In women with symptoms, the usual presentation consists of a yellowish-green frothy vaginal discharge (pictured) that may have a musty odor. Vaginal itchiness is also common. Other symptoms may include lower abdominal pain, pain with urination, and pain during intercourse (dyspareunia). Symptoms often worsen around menstruation (one’s period). The vagina and cervix can be swollen and irritated (“strawberry cervix”).
How’s it Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by examining the vaginal discharge under a microscope. Trichomonas is a pear-shaped protozoa with a tail (flagellate). This picture is a view of an infected cervix and vaginal discharge as seen through the speculum.
How’s it Treated?
Even though this infection is not a bacteria, it can be cured with the an antibiotic. The cure rate is 95%, but the sexual partner also needs treatment at the same time to prevent re-exposure and reinfection. The antibiotic used, metronidazole (Flagyl) causes nausea and vomiting if taken with alcohol.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Abstinence or consistent and correct condom use will prevent transmission of this parasite from one person to the next.
Additional Information
Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
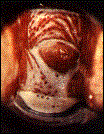
BV may present with a variety of symptoms or none at all. More than 50% of women with BV may be without symptoms. Commonly, though, BV causes an unpleasant fishy or musty vaginal odor, profuse vaginal discharge (usually thin gray or white that sticks to the vagina walls), and vaginal itching and irritation. BV has been associated with Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID).
Diagnosis is made on examination. A pelvic exam is done and a sample of the milky discharge is obtained (pictured is the discharge on the vagina). Under the microscope, the cells of the vagina have a classic appearance in Bacterial Vaginosis (“Clue cells”). In addition, there is a strong fishy odor when the sample is mixed with potassium hydroxide (the “whiff test” is where the doctor smells the vaginal discharge to see if that odor is present.)
 Obtaining a sample of the discharge |
 The whiff test |
How’s it Treated?
Treatment is with an antibiotic (metronidazole or clindamycin) taken orally or vaginally. As noted above, it is unclear if BV is sexually transmitted. Some authorities feel treatment of all sexual partners is crucial in preventing reinfection, though scientific studies have not consistently proven this.
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
It is unclear if this infection is obtained by sexual relations. Women who are sexually active have this disease much more commonly than those abstaining from sexual relations. Regular and correct condom use may protect against this infection though it has not been proven in studies.
VAGINAL YEAST
Vaginal yeast infections are the second most common cause of vaginal discharge in the United States (the first is Bacterial Vaginosis). Yeast infection is not considered a sexually transmitted disease, but is included here because it is such a common cause of vaginal discharge. Candida yeast can be found in the vaginas of almost one in every two woman of childbearing age though the majority of these women have no symptoms unless something occurs to disrupt the normal vaginal environment (see below). The vast majority of yeast infections are caused by the Candida albicans species.
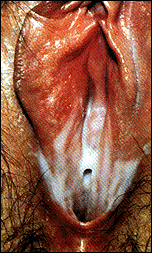
Common Signs & Symptoms
Vaginal itchiness and a cottage cheese-like discharge are the most common symptoms of a yeast infection. The vagina and labia can be red, swollen, sore, and quite irritated. Burning with urination and pain during intercourse (dyspareunia) are also common complaints. Odor, if present, is minimal (in contrast to the fishy odor of bacterial vaginosis).
How’s it Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made on examination. A pelvic exam is done and a sample of the discharge is obtained (pictured is the curd-like discharge as seen through a speculum during pelvic examination). A sample of the discharge is often viewed under the microscope and reveals the yeast organisms. Looking under a microscope also helps rule out other causes of discharge (e.g., bacterial vaginosis, trichomonas) that would require different treatment.
How’s it Treated?
Treatment is with an antifungal medication of which there are many. Over-the-counter creams and vaginal suppository medications are available without a doctor’s prescription and include clotrimazole (Gynelotrimin, Mycelex), butoconazole (Femstat), and miconazole (Monistat). An oral antifungal, fluconazole, is commonly prescribed by physicians as it is a one time dose with minimal side effects (including ease of administration; one pill and not a number of days applying something onto or into one’s vagina). Yeast infections are not considered sexually transmitted, and therefore sexually partners do not need treatment ( though it is interesting to note that 1 in 5 men whose partners had a yeast infection were found to have microscopic yeast present in their urethras).
How do I avoid Getting It (Prevention)?
Though not currently believed to be sexually transmitted, yeast infections are associated with a number of medications and personal states. Avoidance of these will decrease your chance of getting a yeast infection. One of the most common cause of yeast infections is the use of an antibiotic. In addition to destroying bacteria that cause illness, antibiotics kill off the “good” bacteria that normally live in the vagina. Without the normal lactobacillus bacteria in the vagina, yeast cells can take-over and grow out-of-control. This is why some woman douche with yogurt. Unpasturized yogurt contains the “good” bacteria that are normally found in the vagina. It is unclear, however, if douching with yogurt helps or hurts, and we do not recommend trying this without first checking with your doctor. Vaginal yeast infections are just one more reason why antibiotics should be avoided except in the treatment of a bacterial infection (e.g., and not for the treatment of colds and flu – which are caused exclusively by viruses upon which an antibiotic will have no effect). Also, douching with vinegar or other chemicals has been shown to increase the rate of vaginal yeast infections. This is likely a result of the same process that occurs with antibiotics: the “good” bacteria living in the vagina are destroyed by the douche, leaving the yeast to grow and multiply.
Yeast infections are quite common during pregnancy. It is believed this is due to a chemical change in the vaginal environment (essentially there is more sugar in the vaginal juices on which the yeast feed). Similarly, people with diabetes (a disease of sugar metabolism) also get yeast infections more frequently.
It has been shown than tight fitting, poorly ventilated clothing and non-cotton undergarments result in an increase in groin warmth and moisture (sweat), and can lead to yeast infections. This is one reason yeast infections are more prominent in the warmer tropical and sub-tropical climates.
Additional Information
Get additional information on this and other diseases by clicking here.
CONDOMS
As far back as 1350 BC, there are records of Egyptian men wearing sheaths as decorative covers for their penises. In the eighteenth century, condom use became popular for protection against infections and unwanted pregnancies. The condom is usually made of latex rubber (another name for it is “a rubber”) and is meant to fit an erect penis. Many condoms come lubricated and/or premedicated with spermicide (a chemical that kills sperm cells on contact). Other condoms made of lamb intestines are more expensive and may not protect as well against sexually transmitted diseases. Condoms are designed to keep semen from getting into the woman’s vagina. To maximize the protective benefits of condoms, they must be used correctly.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Condoms usually come rolled up in a package. It will unroll to about 7 1/2 inches, though one should not unroll it until putting it on the erection. A 1 3/8 inch ring is found on the open end to help prevent the condom from slipping off during use. The closed end often has a nipple reservoir that catches semen and helps prevent the condom from breaking. A high-quality latex condom has a failure rate of 1% – 2%, meaning that one can expect their condom to break, burst, contain a minute hole, or slip off, once or twice every 100 times of use. Because of this, only abstinence is completely effective at preventing STDs.
To use a condom correctly, pinch the end (the nipple) to get the air out prior to placing it on the head of the penis. This pinched-off space will be where the ejaculate collects and minimizes the risk of bursting the condom. Roll the condom down the shaft of the erection, covering as much skin as possible (many STDs can spread from skin to skin contact even if there are no open sores or rashes present). The condom must be unrolled onto the erection before any intercourse occurs as it is common to leak a small amount of semen from the stimulated penis prior to ejaculation. If you are not using a lubricated condom, you should put K-Y Jelly or a spermicide onto the condom once it has been placed on the erection to lubricate and hence minimize the risk of tearing the condom during sexual relations. NEVER use Vaseline (petroleum jelly) on the condom as it can dissolve the latex. When withdrawing the condom-covered penis from the vagina or mouth, be sure to hold the rim to prevent it from slipping off and spilling sperm onto mucous membranes. In case of an accidental spill around or in the vagina, insert spermicide cream, jelly, or foam gently in and around the vagina. Do not douche.
Condoms can be bought at any drugstore, and usually come packaged in sets of 3 to 12. To order condoms-by-mail, discretely and inexpensively, check out our hardcopy male genitalia kit, or click on the condom picture.
RESOURCES
This online guide has discussed the most common sexually transmitted diseases seen today. It has shown you detailed photographs and given information on the common signs & symptoms of these STDs and STIs. The STD Online Guide reviews how the diseases are diagnosed, how they are treated, and how to prevent catching them in the first place. We hope this guide has has helped you learn about these illnesses, and how best to avoid them in the future. As noted, it is important to see your own physician if you believe you might have one of these infections. There is no substitute for a good history and physical exam by a qualified professional.
For more detailed information, there are a number of excellent books that you can get delivered to your home practically overnight. In most cases, you can be reading our recommended books within a day or two, so consider enhancing your knowledge base by ordering one or more of the following.
- Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC) – review of STD rates & other cool information.
- Choices : Sex in the Age of Stds (by Jeffrey A. Nevid) Information on how to have safe sex “in the age of STDs”
- Everything You Need to Know About Stds: Sexually Transmitted Disease (Need to Know Library) – for all ages. (by Samuel G. Woods)
- Sexually Transmitted Disease Sourcebook: Basic information about Herpes, Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Hepatitis, Nongonoccocal urethritis, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, and more. (Eds. L. Ross & P. Dresser)
- Color Atlas and Synopsis of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (by Hunter Handsfield)
- Sex, Disease, and Society: A Comparative History of Sexually Transmitted Diseases and HIV/AIDS in Asia and the Pacific (by Milton James Lewis (Ed.))
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases and AIDS (by David Daniels)
Below is also an extensive list of other websites with additional information and details on each of the topics presented herein. If you have found a site that you believe has good information, please let us know.
Thank you again for supporting AfraidToAsk.com. We hope you have found this guide helpful and informative.